
At the Equator, the Earth's gravity is 9.780 m/s 2 and at the poles it is 9. The last section presents empirical evidence supporting the notion that the gravity equation is a reduced form from a partial equilibrium subsystem of a general equilibrium model with nationally differentiated products. The effect of latitude on gravitational force is relevant as gravity increases with increasing distance from the Equator. suggests, the typical gravity equation is misspecified, omitting certain price variables.At higher altitudes, gravity decreases slightly.This figure is based on a measure of gravity at sea level at a latitude of 45°. In this example, a 3 kilogram mass, at a height of 5 meters, while acted on by Earth's gravity would haveġ47.15 Joules of potential energy, PE = 3kg * 9.81 m/s 2 * 5m = 147.15 J.ĩ.81 meters per second squared (or more accurately 9.80665 m/s 2) is widely accepted among scientists as a working average value for Earth's gravitational pull. Gravitational potential energy is one type of potential energy and is equal to the product of the object's mass (m), the acceleration caused by gravity (g), and the object's height (h) as distance from the surface of the ground (the body).
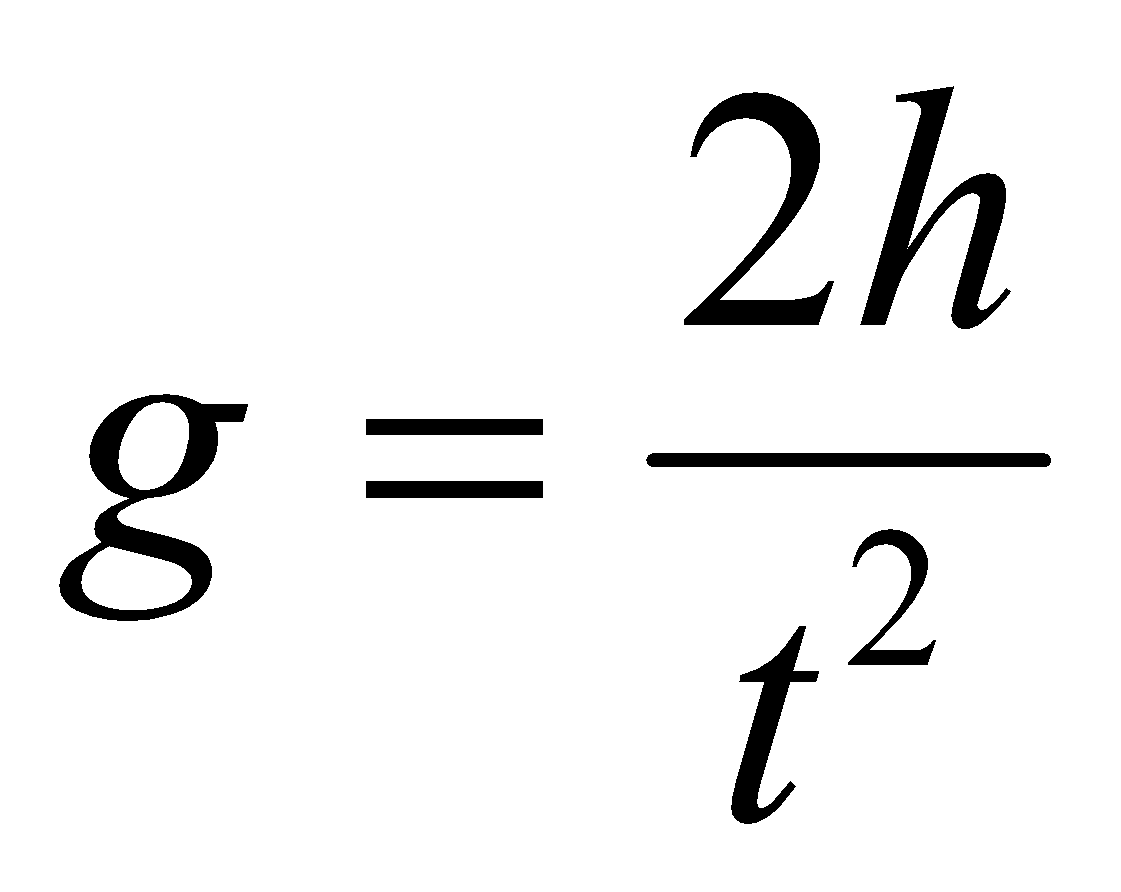
Potential Energy is the stored energy of an object given its position relative to a body.

What Is Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE)
You can work out this force and you'll get 2.8 × 10 -7 newton.

The satellites or objects become weightless,this produce lot of difficulties. Inserting these values into the equation to get 6.67 × 10 -11 newton square metre kilogram -2 × 60 kilogram × 70 kilogram 1 metre 2. Gravity Equation F force of gravity G gravitational constant (610-11) 0.00000000006 M1 mass of body 1 M2 mass of body 2 S2 distance between M1. Artificial gravity is produced by rotating a space craft about its own axis. Suppose: your mass, m, is 60 kilogram the mass of your colleague, M, is 70 kg your centre-to-centre separation, r, is 1 m and G is 6.67 × 10 -11 newton square metre kilogram -2. This leaves us with an equation for the acceleration of gravity. We can do this quite simply by using Newton's equation: force gravity = G × M × m separation 2. The gravitational field strength - g - describes the amount of force exerted upon every. Suppose you want to calculate the size of the gravitational force acting between you and your colleague as you approach each other (one metre apart) in the corridor.
GRAVITY EQUATION HOW TO
Find out how to calculate gravitational forces


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
